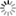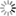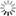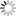Free energy calculation combined with molecular dynamics simulation
Kazushi Fujimoto
Graduate of School of Engineering,
Nagoya University

Solubilization, membrane penetration, binding between virus capsid and receptor are caused by intermolecular interaction between these molecules. Free energy analysis is effective tool in order to clarify physic chemically the penetration or binding.
We develop molecular dynamics (MD) software, which can calculate the free energy, in order to obtain free energy profile between the virus capsid and receptor. The free energy profile of a methane and water molecule penetrating into a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micelle was calculated by our MD software.
Figure shows the calculated mean force and free energy profile. In Fig. (b), the mean force of the methane molecule at r = 2 nm is attractive to a large degree. It is found that the methane is taken into the SDS micelle by this attracting force. On the other hand, the mean force of the water molecule within a range of 0.5 to 2 nm was repulsive force. Therefore, the water molecule dose not penetrates into the SDS micelle core. In Fig. (c), the methane molecule can penetrate into the SDS micelle without free energy barrier, and move about there. The water molecule cannot penetrate into the SDS micelle because of highly unstable.
The position and strength of connection can be clarified by using the free energy profile. The free energy of profile between the virus capsid and the receptor will be calculated.
|
(a) Number density of the hydrophobic (green line) and hydrophilic (lite green line) of the SDS micelle and the water molecules (purple line). (b) Mean force and (c) free energy profile of the methane (red dot) and water (○) molecules. ― and □ represent our previous |